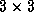 pixel box centred on the brightest
pixel in a specified region and reports the fitted location and
intensity.
pixel box centred on the brightest
pixel in a specified region and reports the fitted location and
intensity.
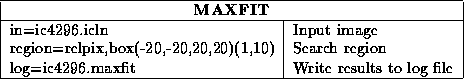
In this example, we fit a Gaussian to a region of an image by inputting
the region in a file. The file was generated interactively by
cgcurs
(see Chapter 16); you delineate a polygonal
region around the source of interest with a cursor. The quality of your
fit can improve significantly by selecting a snug region, and/or using
the clip keyword to keep pixel values with little signal (e.g.
sidelobes and noise) out of the fitting process.
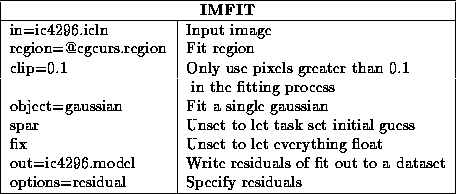
Task imfit
can fit multiple components. In this case, you
will need to set good initial estimates of the source parameters with
the spar keyword, and good values for region and clip
become more important.
Note that if you specify a coordinate in km s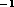 then the keyword
stype indicates what convention that coordinate is in (radio or
optical). You can specify the spectral-axis coordinate in any of
frequency and the two velocity conventions, regardless of what the
header says the spectral axis is; all spectral axis conversions are done
as needed. In addition, any spectral-axis coordinate is converted to
each of frequency, and optical and radio convention velocities (if
possible).
then the keyword
stype indicates what convention that coordinate is in (radio or
optical). You can specify the spectral-axis coordinate in any of
frequency and the two velocity conventions, regardless of what the
header says the spectral axis is; all spectral axis conversions are done
as needed. In addition, any spectral-axis coordinate is converted to
each of frequency, and optical and radio convention velocities (if
possible).
See the help file for all the choices.
