Having no distinction between single- and multi-source files has the advantage that all visibility tasks can manipulate any visibility dataset. However manipulating a dataset with, say, several sources can require more care on the part of the user. For example, it rarely makes sense to make an image using data from several sources. Generally the user is given reasonable flexibility to perform whatever s/he deems appropriate -- but this has some disadvantages. For example, consider determining calibration for an observation where the calibrator (a point source) and the program source are within the one dataset. In deriving the antenna gains, you would want to select only the data from the calibrator, whereas when imaging you would select only the data from the program source. The visibility selection mechanism (see Section 5.5) handles this situation. But to forget to select the appropriate data (calibrating with data including the program source, or imaging including the calibrator) would result in a mess.
Thus, for example, if the calibrator was 0823-500 , and the program source was vela, one would use
select=source(0823-500)and
select=source(vela)to select the appropriate source.
The selection criteria most appropriate for datasets containing multiple sources, frequencies and mosaiced pointing centres are source, frequency, window, ra, dec, dra and ddec.
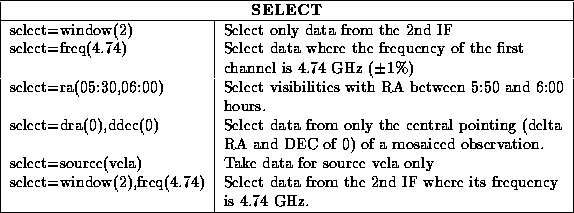
Other examples of using the select keyword are given below:
