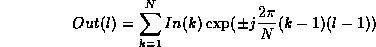
There are three FFT routines, namely:
subroutine fftrc(in,out,sign,n)
subroutine fftcr(in,out,sign,n)
subroutine fftcc(in,out,sign,n)
These perform one-dimensional FFTs. In all cases, sign is the sign
of the exponent in the transform (i.e. a sign of -1 is conventionally
viewed as a forward transform), and n is a power of 2 giving the
length of the (full) sequence.  scaling is never performed
(it is up to you to scale at the best time). In is the input
array, and out is the output array. These routines
evaluate:
scaling is never performed
(it is up to you to scale at the best time). In is the input
array, and out is the output array. These routines
evaluate:
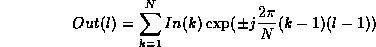
where k and l vary from 1 to N.
Fftrc transforms a real
sequence (i.e. in is a real array) and outputs only the first 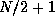 complex values. No information is lost because of the conjugate
symmetry of FFTs of real sequences. Conversely fftcr takes a
complex sequence of length
complex values. No information is lost because of the conjugate
symmetry of FFTs of real sequences. Conversely fftcr takes a
complex sequence of length 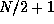 and produces a real sequence of length N.
Finally fftcc performs a complex to complex transform, with
both input and output being of length N.
and produces a real sequence of length N.
Finally fftcc performs a complex to complex transform, with
both input and output being of length N.